Hello OApp with Hardhat
Walkthrough
Introduction
In this Recipe we transfer a message from one chain to another. We choose Sepolia (Ethereum's testnet) and Amoy (Polygon's testnet) as the sending and receiving chain respectively.
OApp is short for Omnichain application and is a generic message passing contract interface provided by LayerZero to send and receive arbitrary data across chains.
This interface and be extended and/or customized according to whatever logic is required by your specific application.
Tech stack
create-lz-oapp- typescript
- nodejs
- solidity
- hardhat
Guide
Setup project
npx create-lz-oapp@latest
Answer the questions that follow in the prompt
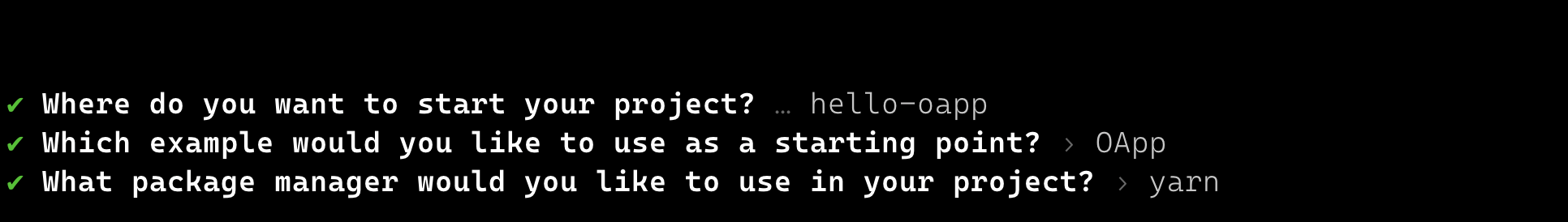
LayerZero projects are Node.js projects with both the Hardhat and Foundry development frameworks installed. We will be using Hardhat for this guide.
The package comes with a pre-built sample OApp contract named MyOApp.sol inside /contracts/ directory.
Update configs
By default the config created via create-lz-oapp comes with sepolia, fuji and amoy defined. For our purposes since we only care about sepolia and amoy we can make sure our hardhat.config.ts looks something like this:
It won't matter if you want to keep fuji in the config. We are removing it for now just so it's cleaner
// ...
// ... (no changes from default)
// ...
const config: HardhatUserConfig = {
// ...
// ... (no changes from default)
// ...
networks: {
sepolia: {
eid: EndpointId.SEPOLIA_V2_TESTNET,
url: process.env.RPC_URL_SEPOLIA || 'https://rpc.sepolia.org/',
accounts,
},
// removed `fuji` network from here
amoy: {
eid: EndpointId.AMOY_V2_TESTNET,
url: process.env.RPC_URL_AMOY || 'https://polygon-amoy-bor-rpc.publicnode.com',
accounts,
},
},
// ...
// ... (no changes from default)
// ...
};
export default config;
See here for the full config file
and layerzero.config.ts looks something like this:
// ...
// ... (no changes from default)
// ...
const sepoliaContract: OmniPointHardhat = {
eid: EndpointId.SEPOLIA_V2_TESTNET,
contractName: 'MyOApp',
};
// ...
// ... (removed fuji contract object)
// ...
const amoyContract: OmniPointHardhat = {
eid: EndpointId.AMOY_V2_TESTNET,
contractName: 'MyOApp',
};
const config: OAppOmniGraphHardhat = {
contracts: [
{
contract: sepoliaContract,
},
// removed fuji contract object
{
contract: amoyContract,
},
],
connections: [
// ...
// ... (removed all objects and keep only
// ... sepolia -> amoy and amoy -> sepolia)
// ...
{
from: sepoliaContract,
to: amoyContract,
},
{
from: amoyContract,
to: sepoliaContract,
},
],
};
export default config;
See here for the full config file
Add .env variables
Refer to .env.example for the required .env variables. Note: Either one of MNEMONIC or PRIVATE_KEY is required.
Create a .env file and add your variables in there.
MNEMONIC="test test test test..." # only one of MNEMONIC or PRIVATE_KEY required
PRIVATE_KEY="" # only one of MNEMONIC or PRIVATE_KEY required
RPC_URL_SEPOLIA=""
RPC_URL_AMOY=""
Test and Deploy Contracts
Test
npx hardhat test
Deploy
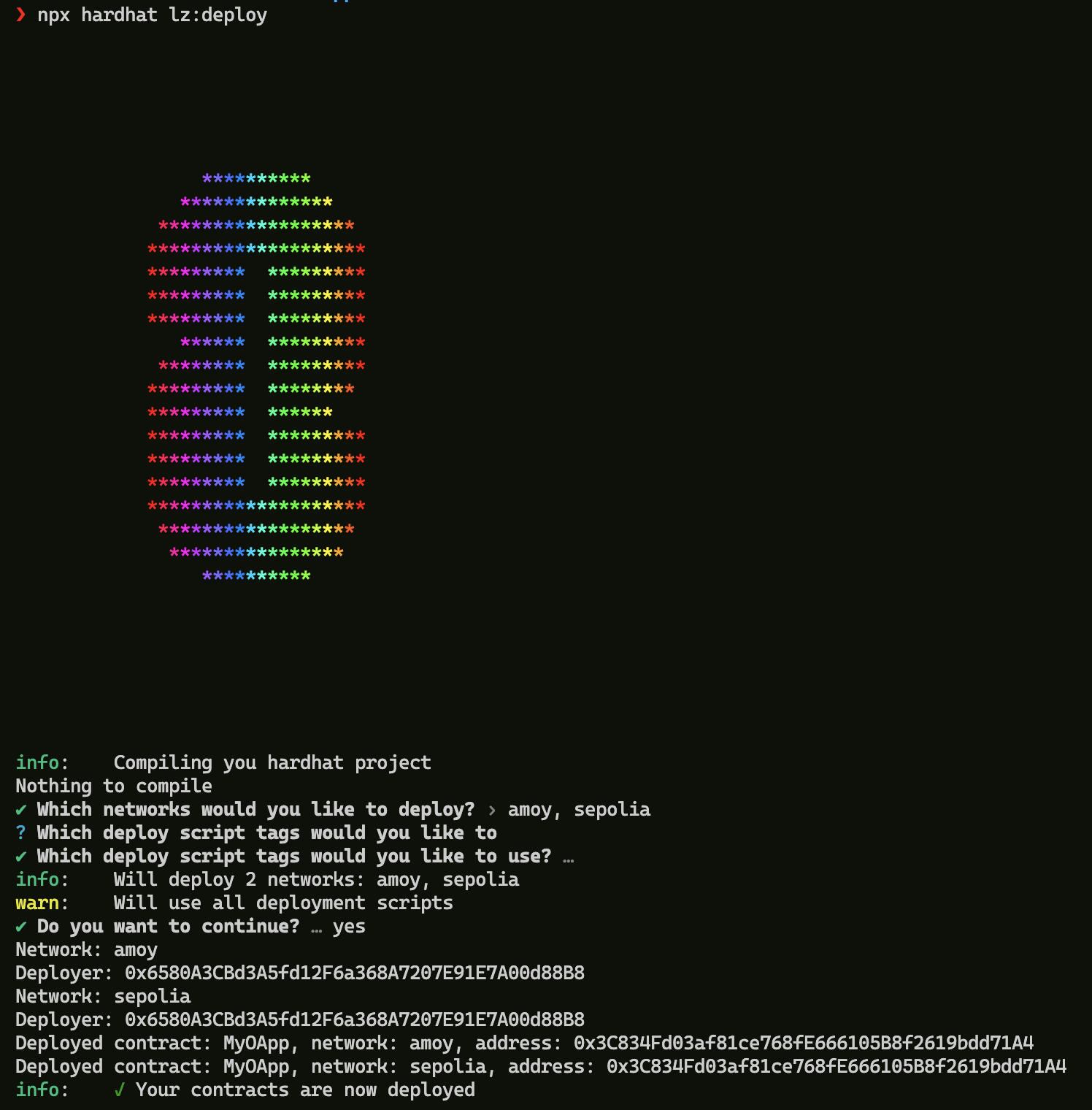
We'll be using the lz:deploy hardhat task that comes packaged in the project with create-lz-oapp that looks into the config files (hardhat.config.ts and layerzero.config.ts) to deploy contracts on all configured chains. Eg., for our project the task will deploy MyOApp.sol on both sepolia and amoy networks.
npx hardhat lz:deploy
Output on your terminal should look something like this:
Wire Up Contracts
The concept of wiring up contracts is about telling the Contract instances on two separate chains about each other. create-lz-oapp comes pre-configured with a bunch of helpful hardhat tasks that can help you wire up the contracts once deployed.
For a detailed overview of all possible configuration commands, see Configuring Contracts.
Every single time layerzero.config.ts is updated, the peers must be updated (calling setPeer on the contracts)
Execute the following in the terminal:
npx hardhat lz:oapp:wire --oapp-config layerzero.config.ts
This function will call setPeer on each contract instance, as well as implement the custom configurations added.
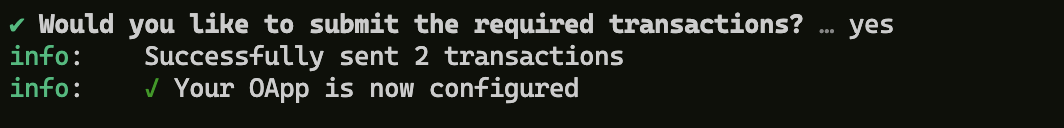
Executing this command will first ask you if you want to preview the transaction before executing:
The preview will look something like this:
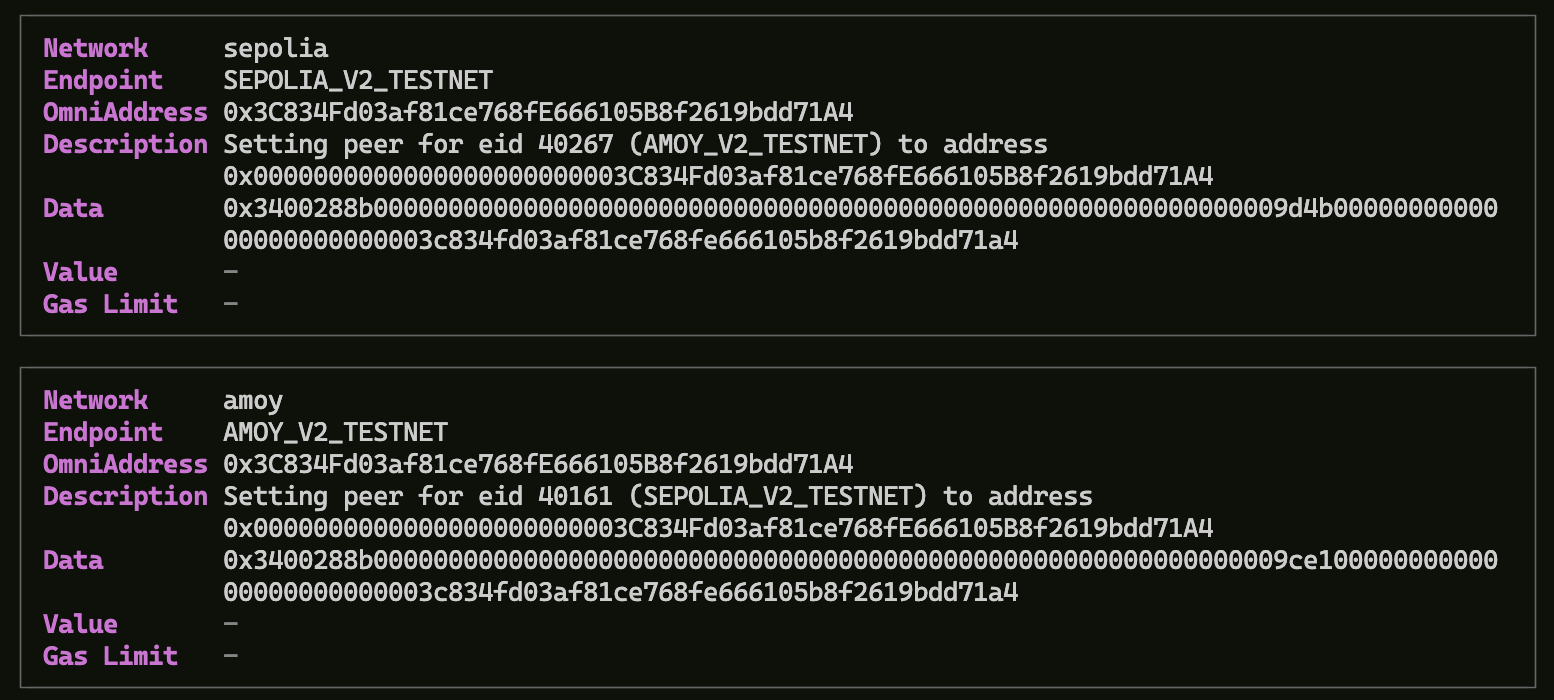
The next prompt will ask you to sign on the transaction, if you respond yes, the two transactions are sent on the chains configured in layerzero.config.ts
Add a new Hardhat task
We create a new hardhat task to send a message between two chains:
import {task} from 'hardhat/config';
import {
createGetHreByEid,
createProviderFactory,
getEidForNetworkName,
} from '@layerzerolabs/devtools-evm-hardhat';
import {Options} from '@layerzerolabs/lz-v2-utilities';
// send messages from a contract on one network to another
task('oapp:send', 'test send')
// contract to send a message from
.addParam('contractA', 'contract address on network A')
// network that sender contract resides on
.addParam('networkA', 'name of the network A')
// network that receiver contract resides on
.addParam('networkB', 'name of the network B')
// message to send from network a to network b
.addParam('message', 'message to send from network A to network B')
.setAction(async (taskArgs, {ethers}) => {
const eidA = getEidForNetworkName(taskArgs.networkA);
const eidB = getEidForNetworkName(taskArgs.networkB);
const contractA = taskArgs.contractA;
const environmentFactory = createGetHreByEid();
const providerFactory = createProviderFactory(environmentFactory);
const signer = (await providerFactory(eidA)).getSigner();
const oappContractFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('MyOApp', signer);
const oapp = oappContractFactory.attach(contractA);
const options = Options.newOptions().addExecutorLzReceiveOption(200000, 0).toHex().toString();
const [nativeFee] = await oapp.quote(eidB, 'Hello World', options, false);
console.log('native fee:', nativeFee);
const r = await oapp.send(eidB, 'Hello World', options, {
value: nativeFee,
});
console.log(`Tx initiated. See: https://layerzeroscan.com/tx/${r.hash}`);
});
if pasting the above in your /tasks/index.ts results in a dependency error, try installing @layerzerolabs/devtools-evm-hardhat
pnpm i @layerzerolabs/devtools-evm-hardhat
Import tasks in your hardhat config:
...
...
import './tasks'
...
...
Before Testing
How would we know the cross-chain messaging worked?
From inside our deployments folder (/deployments/sepolia/MyOApp.json) we can view the deployment addresses for the contract on both sepolia and amoy.
We will now add a new hardhat task (in the same file as before) in /tasks/index.ts that will read the data string from the contract.
task('oapp:read', 'read message stored in MyOApp')
.addParam('contractA', 'contract address on network A')
.addParam('contractB', 'contract address on network B')
.addParam('networkA', 'name of the network A')
.addParam('networkB', 'name of the network B')
.setAction(async (taskArgs, {ethers}) => {
const eidA = getEidForNetworkName(taskArgs.networkA);
const eidB = getEidForNetworkName(taskArgs.networkB);
const contractA = taskArgs.contractA;
const contractB = taskArgs.contractB;
const environmentFactory = createGetHreByEid();
const providerFactory = createProviderFactory(environmentFactory);
const signerA = (await providerFactory(eidA)).getSigner();
const signerB = (await providerFactory(eidB)).getSigner();
const oappContractAFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('MyOApp', signerA);
const oappContractBFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('MyOApp', signerB);
const oappA = oappContractAFactory.attach(contractA);
const oappB = oappContractBFactory.attach(contractB);
const dataOnOAppA = await oappA.data();
const dataOnOAppB = await oappB.data();
console.log({
[taskArgs.networkA]: dataOnOAppA,
[taskArgs.networkB]: dataOnOAppB,
});
});
When we will execute the send transaction from one chain to another, we will be calling the send function on our contract on network A. This function sends the cross-chain transaction to the contract B deployed on network B. (The contract already knows about contract B because we have executed setPeers)
function send(
uint32 _dstEid,
string memory _message,
bytes calldata _options
) external payable returns (MessagingReceipt memory receipt) {
bytes memory _payload = abi.encode(_message);
receipt = _lzSend(_dstEid, _payload, _options, MessagingFee(msg.value, 0), payable(msg.sender));
}
We will now execute oapp:read task to query the data variable on both chains:
❯ npx hardhat oapp:read --contract-a 0x3C834Fd03af81ce768fE666105B8f2619bdd71A4 --network-a sepolia --contract-b 0x3C834Fd03af81ce768fE666105B8f2619bdd71A4 --network-b amoy
The output should be the default value of data:
{
dataOnOAppA: 'Nothing received yet.',
dataOnOAppB: 'Nothing received yet.'
}
How would we know the transaction worked?
After executing send, the dataOnOAppB should equal Hello World (or whatever message we decide on sending)
Test transfer
Execute the script by running the following command:
npx hardhat oapp:send --contract-a CONTRACT_ADDRESS_ON_NETWORK_A --network-a sepolia --network-b amoy --message "Hello World"
We are sending the message 'Hello World'. The transaction will be executed on network A (sepolia) and will be propagated onto network B and we will confirm by querying data variable on network B to see if it now equals Hello World
We will now execute oapp:read task to query the data variable on both chains:
❯ npx hardhat oapp:read --contract-a 0x3C834Fd03af81ce768fE666105B8f2619bdd71A4 --network-a sepolia --contract-b 0x3C834Fd03af81ce768fE666105B8f2619bdd71A4 --network-b amoy
The output should be the default value of data:
{
dataOnOAppA: 'Nothing received yet.',
dataOnOAppB: 'Hello World'
}
❗ Some Gotchas
-
when running the hardhat task make sure you make the params hyphenated (
contractAbecomescontract-a) -
All deployments that are created from
lz:deploytask are stored in the/deploymentsfolder (this can be added to your committed to your git repository or ignored depending on your use case) -
Sometimes the
nativeFeesent in thevalueparam of thesendtransaction needs to be cranked up by 20-30% to allow some buffer. -
The transaction hash that the task outputs might take a while (sometimes 10-20 minutes) to index on the source/destination chain
-
If there's a node version error try switching over to nodejs v18